Infertility is a disease of the male or female reproductive system defined by the failure to achieve a pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected sexual intercourse. This is a global health issue affecting millions of people of reproductive age worldwide.

Infertility may occur due to male factors, female factors, a combination of male and female factors or may be unexplained.
Fertility counselling provides a safe and confidential space for an individual or a couple to talk freely and openly about their feelings and experiences around potential parenthood in a non-judgmental environment. It can help to make sense of the emotions that are experienced, and explore the discussions, decisions and difficulties that might be part of the fertility journey.
It can cover a range of issues including grief and loss, options and implications of assisted reproduction, using donor eggs or sperm, exploring IVF options. It can help to make the best decisions for them at any stage of their treatment.


Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) is a screening test offered during pregnancy to see if the baby is at risk for having genetic disorders such as Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome) and trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome).
Most NIPT tests screen for:
- Down syndrome
- Trisomy 18
- Trisomy 13
- Disorders affecting sex chromosomes
For the test, the doctor will take a sample of pregnant mother’s blood and send to the lab to look for abnormalities in the fetus’ DNA.

Why is NIPT done?
NIPT helps to determine the likelihood for the fetus to be born with certain chromosomal disorders. It is recommended if:
- Patient has a child with chromosomal abnormality
- There is an ultrasound showing that the fetus may have an abnormality
- There was an earlier screening test which suggests a potential problem
NIPT testing can be done as early as 10 weeks of pregnancy through delivery. It is about 99% accurate in detecting Down syndrome, but it is slightly less accurate for detecting trisomy 18 and 13. Overall, NIPT tests produce fewer false positives than other prenatal screenings. NIPT tests are safe, and there is no risk to the fetus. It requires drawing blood from the pregnant mother only. Having a NIPT test is optional. Your healthcare provider will provide information about prenatal genetic testing and help to make an informed choice about your options.
A Pap smear is a screening procedure for cervical cancer. It tests for the presence of precancerous or cancerous cells on your cervix, which is the opening of the uterus. Regular Pap smear screenings reduce cervical cancer rates and mortality by 80%. During the procedure, cells from cervix area are gently scraped away and examined to look for abnormal growth. The procedure can be done at clinic setting. It may be mildly uncomfortable, but does not usually cause any long-term pain.
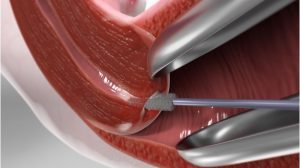
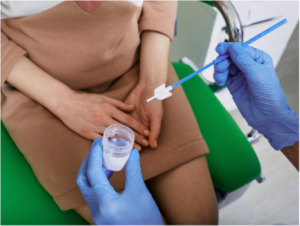
Who needs Pap smear?
It is recommended that Pap smear screening should be done for sexually active women between age 21 to 65 years old.
The initial screening interval is yearly for two years. If the results were normal, then a 3-yearly Pap smear screening is indicated. If cytology and HPV testing are done together and both results are negative, then the cervical screening can be done every 5 years.

Preparation for the Pap Smear
- Do not douche or insert any form of medication (suppositories) into the vagina 24 hours prior to the procedure.
- Avoid sexual intercourse within a period of 24 hours prior to the procedure.
- Avoid taking Pap smear during menstruation.
- Pap smear can be done during pregnancy.
Since Pap smears go more smoothly if the body is relaxed, it is important to stay calm and take deep breaths during the procedure.
- Pap Smear Screening
- Fertility Caunselling
- Urine Pregnancy Test
- Family Planning (Contraception, IUCD, Implanon)
- Antenatal and Postnatal Care
- Investigation and Screening of Fertility
- 4D Screening
- Hormone Replacement Therapy
- Fetal Well-being Scan
- Vaginal Rejuvenation


